Appearance
react 基础-组件的三大核心
state
state 是用来记录数据,并触发更新页面显示
js
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = React.useState(0);
function handleClick() {
setCount(count + 1);
}
return <button onClick={handleClick}>点击了{count}次</button>;
}- 先从 React 引用 useState(), React.useState(初始值) 返回的是一个数组,第一个是当前的 state(count),第二个是更新 state 的对应函数(setCount),命名随意,一般第二个都是在第一个的基础上加上一个 set
- 初始值可以是任何形式的值,比如数字、字符串、数组、bolean 值、对象等,一般初始值要跟最后要设置的值保持一个类型
- 当要改变 count 的值时,调用 setCount 来设置
- setCount 是一个异步执行了,即调用了 setCount 后,不会更改现有渲染中的变量 count,但会请求一次新的渲染。也就是 setCount 后去获取 count 的值,是还不会变的。要监控更新完成了,可以用 Hook useEffect()去监控 count。
- state 是数组和对象时,不要直接修改一个对象或者数组,而要为它创建一个新对象或者数组,并通过把 setXX 设置成这个新对象或者数组来触发重新渲染。一般可以通过{...state}来生成新对象,数组的话可以通过[...arr]、filter()、slice()、map()来返回一个新数组
- setCount 会引起重新渲染,当重新渲染一个组件时,React 会再次调用组件函数。
- setCount(count=>count+1)可以传入一个函数,可以多次更新 state
props
- 每个组件对象都会有 props(properties 的简写)属性
- 组件标签的所有属性都保存在 props 中,通过标签属性从组件外向组件内传递变化的数据,props 变化了,组件也会重现渲染。
- props.children 这个可以拿到组件内的标签体内容
- 组件内部不要修改 props 数据
js
function MyCompont(props) {
console.log("MyCompont props", props);
return (
<div>
<h1>props_传参</h1>
<Person name="小李" age={18} hobbys={["写代码", "打游戏"]} />
<Person name="小王" age={20} hobbys={["看电影", "打篮球"]} />
</div>
);
}
function Person(props) {
console.log("Person props", props);
const { name, age, hobbys = [] } = props;
return (
<div>
{name}---{age}-- 爱好:
{hobbys.map((item, index) => {
return (
<span>
{item}
{index !== hobbys.length - 1 ? "," : ""}
</span>
);
})}
</div>
);
}js
<script type="text/babel">
/* 此处需要写babel type="text/javascriptt" 因为之前是js代码,但现在写的不是js而是jsx*/
/* 1.定义函数组件 */
function MyCompont(props) {
console.log("MyCompont props", props);
const [count, setCount] = React.useState(0);
function handleClick() {
setCount(count + 1);
}
return (
<div>
<h1>props_传参2_其中一个组件更新后,其它的组件也跟着更新</h1>
<Counter count={count} onClick={handleClick} />
<br />
<Counter count={count} onClick={handleClick} />
</div>
);
}
function Counter(props) {
const { count, onClick } = props;
return <button onClick={onClick}>点击了{count}次</button>;
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
/* 2.将函数式组件渲染到页面上 */
root.render(<MyCompont />);
</script>Context:传递 props 的另一种方法
当需要在组件树中深层传递参数,传递 props 就会变得很麻烦。 最近的根节点父组件可能离需要数据的组件很远,状态提升 到太高的层级会导致 “逐层传递 props” 的情况。 Context 让父组件可以为它下面的整个组件树提供数据。
Prop 逐级透传的效果:
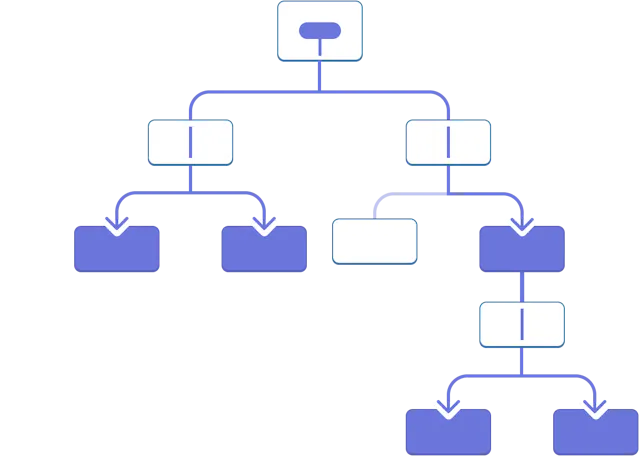
Context 传递
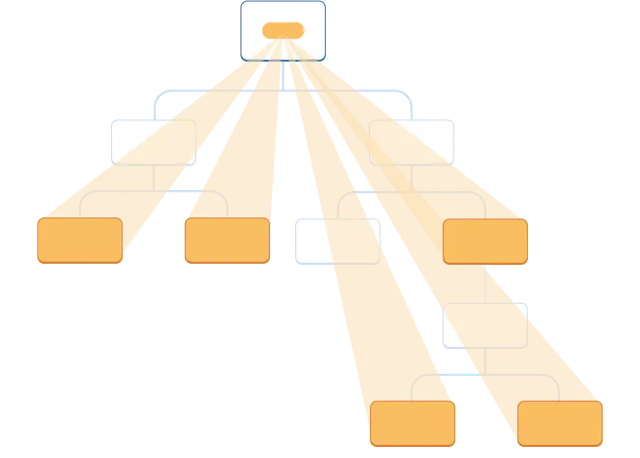
- 第一步,先使用 createContext 创建一个 Context
- 第二步,使用 Context.Provider 传递需要的值
- 第三步,在需要用的地方使用 useContext 接收值
js
<script type="text/babel">
/* 此处需要写babel type="text/javascriptt" 因为之前是js代码,但现在写的不是js而是jsx*/
/* 1.第一步,先创建一个Context */
const ThemeContext = React.createContext("red");
/* 1.定义函数组件 */
function MyCompont() {
console.log("MyCompont in");
const [themeColor, setThemeColor] = React.useState("red");
// 更改主题颜色
function onClickColor(color) {
setThemeColor(color);
}
return (
<div>
当前h3标签颜色:{themeColor}
<br />
<button onClick={onClickColor.bind(this, "red")}>红色</button>
<button onClick={onClickColor.bind(this, "green")}>绿色</button>
<button onClick={onClickColor.bind(this, "yellow")}>黄色</button>
<button onClick={onClickColor.bind(this, "blue")}>蓝色</button>
<button onClick={onClickColor.bind(this, "skyblue")}>天蓝色</button>
{/*2.第二步,使用Context.Provider传递值*/}
<ThemeContext.Provider value={themeColor}>
<Level1></Level1>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
</div>
);
}
function Level1() {
/*3.第三步,在需要用的地方使用useContext接收值*/
const themeColor = React.useContext(ThemeContext);
return (
<div style={{ border: "solid 1px #ccc", width: "80%", margin: 20 }}>
子组件1
<h3 style={{ color: themeColor }}>子组件1的h3</h3>
<Level2 />
</div>
);
}
function Level2() {
const themeColor = React.useContext(ThemeContext);
return (
<div style={{ border: "solid 1px #ccc", width: "60%", margin: 20 }}>
子组件2
<h3 style={{ color: themeColor }}>子组件2的h3</h3>
<Level3 />
</div>
);
}
function Level3() {
const themeColor = React.useContext(ThemeContext);
return (
<div style={{ border: "solid 1px #ccc", width: "40%", margin: 20 }}>
子组件3
<h3 style={{ color: themeColor }}>子组件3的h3</h3>
</div>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
/* 2.将函数式组件渲染到页面上 */
root.render(<MyCompont />);
</script>ref
当希望组件“记住”某些信息,但又不想让这些信息触发新的渲染时,可以使用 ref。
用法: const myRef = React.useRef(初始值) 初始值跟 useState 一样,可以是任何形式的值 useRef 返回一个这样的对象:
js
{
current: xxx; // 向 useRef 传入的初始值
}ref 是一个普通的 JavaScript 对象,current 属性可以被读取和修改的
js
读取:myRef.current
修改:myRe.current = xxx一般使用场景:
- 用来做存储组件内的数据使用,比如一个定时器 id
- 用来访问真实 DOM
- 用来访问一个组件实例。需要借助 forwardRef api 和 useImperativeHandle 实现 ref 的传递和句柄暴露
一般不要在渲染过程中读取或写入 ref.current,读取 ref 的值时,一般加上判断 ref.current 是否为 null 的处理,如 if(ref.current)
js
<script type="text/babel">
/* 此处需要写babel type="text/javascriptt" 因为之前是js代码,但现在写的不是js而是jsx*/
/* 1.定义函数组件 */
function MyCompont() {
const [startTime, setStartTime] = React.useState(null);
const [now, setNow] = React.useState(null);
const intervalRef = React.useRef(null);
function handleStart() {
setStartTime(Date.now());
setNow(Date.now());
clearInterval(intervalRef.current);
intervalRef.current = setInterval(() => {
setNow(Date.now());
}, 10);
}
function handleStop() {
clearInterval(intervalRef.current);
}
let secondsPassed = 0;
if (startTime != null && now != null) {
secondsPassed = (now - startTime) / 1000;
}
return (
<div>
<h1>ref_保存变量</h1>
<h2>时间过去了: {secondsPassed.toFixed(3)}</h2>
<button onClick={handleStart}>开始</button>
<button onClick={handleStop}>停止</button>
</div>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
/* 2.将函数式组件渲染到页面上 */
root.render(<MyCompont />);
</script>js
<script type="text/babel">
/* 此处需要写babel type="text/javascriptt" 因为之前是js代码,但现在写的不是js而是jsx*/
/* 1.定义函数组件 */
function MyCompont() {
const inputRef = React.useRef(null);
function handleClick() {
console.log("handleClick inputRef.current", inputRef.current);
// 链式用法
inputRef?.current?.focus();
}
return (
<div>
<input ref={inputRef} />
<button onClick={handleClick}>让输入框获焦</button>
</div>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
/* 2.将函数式组件渲染到页面上 */
root.render(<MyCompont />);
</script>js
<script type="text/babel">
/* 此处需要写babel type="text/javascriptt" 因为之前是js代码,但现在写的不是js而是jsx*/
/* 1.定义函数组件 */
function MyCompont() {
const playerRef = React.useRef(null);
return (
<div>
<button
onClick={() => {
console.log("playerRef.current", playerRef.current);
}}
>
打印ref
</button>
<br />
<button onClick={() => playerRef.current.handleFunc("play")}>
Play
</button>
<button onClick={() => playerRef.current.handleFunc("pause")}>
Pause
</button>
<br />
<br />
<MyVideoPlayer
ref={playerRef}
src="https://interactive-examples.mdn.mozilla.net/media/cc0-videos/flower.mp4"
type="video/mp4"
width="250"
/>
</div>
);
}
const MyVideoPlayer = React.forwardRef((props, ref) => {
const videoRef = React.useRef(null);
// 暴露给父组件的方法
React.useImperativeHandle(ref, () => ({
handleFunc(status, param) {
console.log("MyVideoPlayer handleFunc", status, param);
switch (status) {
case "play":
videoRef.current.play();
break;
case "pause":
videoRef.current.pause();
break;
}
},
}));
return (
<video width="250" ref={videoRef}>
<source
src="https://interactive-examples.mdn.mozilla.net/media/cc0-videos/flower.mp4"
type="video/mp4"
/>
</video>
);
});
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
/* 2.将函数式组件渲染到页面上 */
root.render(<MyCompont />);
</script>例子
作业
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>作业</title>
<style>
@charset "utf-8";
/* 样式重置 */
h1,
h2,
h3,
h4,
h5,
h6,
header,
hgroup,
hr,
input,
li,
ol,
p,
pre,
td,
textarea,
th,
ul {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
ul,
oll,
li {
list-style: none;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
color: #333;
}
i,
em {
font-style: normal;
}
input,
textarea,
button,
select,
a {
outline: none;
border: none;
}
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
border-spacing: 0;
}
.todo-container {
position: static;
}
.todo-wrap {
width: 520px;
margin: 20px auto;
border: 1px solid #999;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.todo-header {
margin: 10px;
}
.todo-header input {
outline: none;
border: 1px solid skyblue;
height: 40px;
width: 500px;
text-indent: 10px;
}
.todo-header input:focus {
box-shadow: 0 0 10px 2px skyblue;
}
.todo-main {
margin: 10px;
border: 1px solid #999;
border-bottom-width: 0;
width: 500px;
}
.todo-main li {
position: relative;
border-bottom: 1px solid #999;
height: 40px;
width: 500px;
line-height: 40px;
}
.todo-main li:hover {
background-color: #ddd;
}
.todo-main li:hover button {
display: inline-block;
}
.checkbox {
margin-right: 10px;
margin-left: 10px;
}
.btn {
position: absolute;
right: 10px;
display: inline-block;
padding: 5px 12px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 30px;
font-size: 14px;
color: #fff;
background-color: red;
box-shadow: inset 0 1px 0 rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2), 0 1px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);
border-radius: 4px;
}
.btn-hide {
display: none;
}
.todo-footer {
position: relative;
margin: 20px 10px;
height: 40px;
width: 500px;
line-height: 40px;
}
</style>
<script>
function onkeyDown() {
const keycode = window.event.keyCode;
if (keycode === 13) {
alert("按下了回车按键 ");
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="todo-wrap">
第14讲作业说明:<br />
1.输入框输入内容,按确定添加一个要做的事项<br />
2.点击每一个事项右边的删除按钮可删除对应事项<br />
2.点击复选框切换完成/已完成,点击删除已完成就删除所有打勾的事项<br />
<b>注:至少要分两个组件,顶部的输入框必须是一个独立的组件</b>
</div>
<div class="todo-container">
<div class="todo-wrap">
<!-- 头部输入框 -->
<div class="todo-header">
<input
type="text"
onkeydown="onkeyDown()"
placeholder="请输入您的任务名称,按回车键确认"
/>
</div>
<!-- todo列表 -->
<ul class="todo-main">
<li>
<label>
<input type="checkbox" class="checkbox" checked />
<span>吃饭</span>
</label>
<button class="btn btn-hide">点击删除</button>
</li>
<li>
<label>
<input type="checkbox" class="checkbox" />
<span>睡觉</span>
</label>
<button class="btn btn-hide">点击删除</button>
</li>
<li>
<label>
<input type="checkbox" class="checkbox" />
<span>打豆豆</span>
</label>
<button class="btn btn-hide">点击删除</button>
</li>
</ul>
<div class="todo-footer">
<button onClick="" class="btn">删除已完成的任务</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>