Appearance
RN 布局和 常用 API
宽度和高度
width 属性指定元素内容区域的宽度。同样,height 属性指定元素内容区域的高度。 width 和 height 都可以取以下值: auto(默认值)React Native 根据元素的内容计算其宽度/高度,无论是其他子元素、文本还是图像。 pixels 以绝对像素定义宽度/高度。根据组件上设置的其他样式,这可能是节点最终尺寸也可能不是。 percentage 分别以父级宽度或高度的百分比定义宽度或高度。
宽度和高度可以与 flex 结合使用 如,设定某个子元素的高度,另一个子元素设置为 flex:1,就会默认占据剩下的高度
javascript
<View style={{ height: 200, borderColor: "#000000", borderWidth: 2 }}>
<View style={{ height: 150, backgroundColor: "#ff0000" }}></View>
<View style={{ flex: 1, backgroundColor: "#ff00ff" }}></View>
<View style={{ height: "10%", backgroundColor: "#00ffff" }}></View>
</View>flex 排版
RN 使用 flexbox 规则来指定某个组件的子元素的布局。注意控制的是容器中的子元素,不是自己; 用的最多的是 flexDirection、alignItems 和 justifyContent 这个三个样式属性。
先讲下 flex
css 里本身是有弹性布局的;
flex:属性决定元素在主轴上如何填满可用区域;整个区域根据子元素的 flex 值会被分为指定的部分;
javascript
<View style={{height:200,borderColor: "#000000",
borderWidth: 2}}>
<View style={{flex:1,backgroundColor:'#ff0000'}}>
</View>
<View style={{flex:1,backgroundColor:'#ff00ff'}}>
</View>
</View>
<View style={{height:200,borderColor: "#000000",
borderWidth: 2}}>
<View style={{height:150,backgroundColor:'#ff0000'}}>
</View>
<View style={{flex:1,backgroundColor:'#ff00ff'}}>
</View>
</View>Flex Direction
flexDirection 可以决定布局的方向(块元素默认的排列方向),也就是主轴,默认竖直(column)方向,即从上到下,row:将子元素从左到右对齐; 比如说两个并列的按钮
javascript
<View style={{width:300,height:300,flexDirection:'row', borderColor: "#000000",
borderWidth: 2,}}>
<View style={{width:100,backgroundColor:'#ff0000'}}>
</View>
<View style={{width:100,backgroundColor:'#0000ff'}}>
</View>javascript
<View
style={{
height: 300,
borderColor: "#000000",
borderWidth: 2,
justifyContent: "center",
}}
>
<View style={{ height: 100, backgroundColor: "#ff0000" }}></View>
<View style={{ height: 100, backgroundColor: "#0000ff" }}></View>
</View>justifyContent
主轴的排列方向 flex-start(默认值)沿主轴起始位置对齐。 flex-end 沿主轴末尾位置对齐。 center 在主轴上居中对齐。 space-between 均匀分布子元素,将剩余空间平均分配给子元素之间。 space-around 主轴上均匀分布子元素,将剩余空间围绕在每个子元素周围。与 space-between 相比的区别在于,使用 space-around 会导致空间被分配到第一个子元素和最后一个子元素之前和之后。 简单来说:between 空间在元素之间平均,两端是没有空间的,around 空间包裹着元素,即两端也会有空间 space-evenly 主轴方向均匀分布子项。每一对相邻项、主开始边缘和第一项以及主结束边缘和最后一项之间的间距都完全相同。 与 around 的区别,around 的两端的间距小一点,元素之间的间距会叠加;evenly 两端间距和元素之间间距都是一样的,比如购买记录的列表,可能需要这样设置;
javascript
<View
style={{
height: 300,
borderColor: "#000000",
borderWidth: 2,
justifyContent: "center",
}}
>
<View style={{ height: 100, backgroundColor: "#ff0000" }}></View>
<View style={{ height: 100, backgroundColor: "#0000ff" }}></View>
</View>alignItems
容器的子元素沿着次轴的排列方式
stretch:拉伸以匹配容器次轴的高度。想要实现拉伸那么子元素在次轴方向上不能有固定尺寸的; flex-start:对齐到容器次轴的起始位置。 flex-end:对齐到容器次轴的末尾位置。 center:居中对齐于容器次轴上。 baseline:沿着公共基线对齐容器的子元素
javascript
<View
style={{
height: 600,
width: 600,
borderColor: "#000000",
borderWidth: 2,
justifyContent: "center",
alignItems: "center",
}}
>
<View style={{ height: 100, width: 100, backgroundColor: "#ff0000" }}></View>
<View style={{ height: 100, width: 100, backgroundColor: "#0000ff" }}></View>
<View style={{ height: 100, width: 100, backgroundColor: "#00ff00" }}></View>
</View>alignSelf
alignSelf 会覆盖由父级设置的任何使用 alignItems 的选项。
javascript
<View
style={{
height: 600,
width: 600,
borderColor: "#000000",
borderWidth: 2,
justifyContent: "center",
alignItems: "center",
}}
>
<View
style={{
height: 100,
width: 100,
backgroundColor: "#ff0000",
alignSelf: "flex-end",
}}
></View>
<View style={{ height: 100, width: 100, backgroundColor: "#0000ff" }}></View>
<View style={{ height: 100, width: 100, backgroundColor: "#00ff00" }}></View>
</View>flexWrap
flexWrap 用于设置容器的换行方式,它控制了当子元素超出容器在主轴上的尺寸时要如何处理。默认情况下,子元素被强制放置在一行中(这可能会使元素被挤压)。如果允许换行,则项目将根据需要沿主轴分为多行。
在换行时,可以使用 alignContent 来设置这些行在容器中的排列方式
javascript
<View
style={{
height: 500,
width: 600,
borderColor: "#000000",
borderWidth: 2,
justifyContent: "center",
alignItems: "center",
flexWrap: "wrap",
}}
>
<View style={{ height: 100, width: 100, backgroundColor: "#ff0000" }}></View>
<View style={{ height: 100, width: 100, backgroundColor: "#0000ff" }}></View>
<View style={{ height: 100, width: 100, backgroundColor: "#00ff00" }}></View>
<View style={{ height: 100, width: 100, backgroundColor: "#ff00ff" }}></View>
<View style={{ height: 100, width: 100, backgroundColor: "#ff00ff" }}></View>
<View style={{ height: 100, width: 100, backgroundColor: "#00ffff" }}></View>
</View>alignContent
主要用于设置多行显示时,换行后的对齐方式; flex-start(默认值):将换行后的行与容器的次轴起始位置对齐。 flex-end:将换行后的行与容器的次轴末尾位置对齐。 stretch(在 Web 上使用 Yoga 时的默认值):拉伸换行后的行以匹配容器的次轴高度。 center:将换行后的行居中对齐于容器的次轴。 space-between:均匀地在容器的次轴上间隔排列换行后的各个线,使剩余空间平均分布在这些线之间。 space-around:均匀地在容器的次轴上间隔排列换行后各个线,使剩余空间平均分布在这些线周围。相较于使用 space-between,使用 space-around 会导致空白区域被分配到第一条线和最后一条线之前及之后两端。
与 alignItems 类似,那里是针对某个元素,这里是针对行元素,把一行看出一个的感觉
绝对定位和相对定位
与 css 类似的,在日常布局中可以根据自己的习惯使用绝对定位还是相对定位;
position 类型定义了元素在其父元素中的定位方式。 relative(默认值) 默认情况下,一个元素是相对定位的。这意味着一个元素根据布局的正常流程进行定位,然后根据 top、right、bottom 和 left 的值进行偏移。该偏移不会影响任何兄弟或父级元素的位置。位置是相对于自己按照正常流程时定位的位置。 absolute 绝对定位时,一个元素不参与正常布局流程。它独立于其兄弟元素进行布局。位置是基于 top, right, bottom, 和 'left' 值来确定的,相对于元素第一个非绝对定位的父元素;
常用 API
StyleSheet
代码更加简洁,将代码中的样式都用 StyleSheet 来定义 import {StyleSheet} from 'react-native';
javascript
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
alignItems: "center",
},
image: {
position: "absolute",
right: 0,
width: utils.px(960),
height: utils.px(1080),
},
titleView: {
alignSelf: "flex-start",
height: utils.px(164),
paddingLeft: utils.px(110),
justifyContent: "flex-end",
},
});BackHandler
BackHandler API 用于监听设备上的后退按钮事件,可以调用你自己的函数来处理后退行为;
回调函数是倒序执行的(即后添加的函数先执行)。
如果某一个函数返回 true,则后续的函数都不会被调用。 如果没有添加任何监听函数,或者所有的监听函数都返回 false,则会执行默认行为,退出应用。 应用场景:按返回键的时候提交表单,或者注销信息; 怎么用?
javascript
import {StyleSheet,BackHandler} from 'react-native';
componentDidMount() {
LOG('[PackagePay] componentDidMount');
// 注册返回按键的处理
BackHandler.addEventListener('hardwareBackPress', this.onBackClicked);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
LOG('[PackagePay] componentWillUnmount start');
BackHandler.removeEventListener('hardwareBackPress', this.onBackClicked);
}
//在退出的时候执行所有的保存操作,
onBackClicked = () => {
LOG('[PackagePay] backhandler start===============');
LOG(
'[PackagePay] backhandler ',
this.state.focusArea,
this.itemRef[this.state.curPriceIndex]?.state.showDec,
);
//比如说显示了描述内容,按返回键关闭详情
if (this.priceDescShow) {
let ret = this.itemRef?.handleFunc('hideDesc');//隐藏描述内容
if (ret) {
return true;//这里返回true了,会阻止事件冒泡传递,因而不会执行默认的后退行为。
}
}
LOG('[PackagePay] backhandler');
return false; //返回false时,会使事件继续传递,触发其他注册的监听函数,或是系统默认的后退行为,这里就会退出页面
};还有一个方法,exitApp(),直接退出应用,这个后面用的更多的是咱们软终端自定义的一个退出应用方法;
ProgressBarAndroid,
应用场景,如:加载中
javascript
<View style={styles.imageView}>
<ProgressBarAndroid></ProgressBarAndroid>
</View>
imageView: {
width: utils.px(450),
height: utils.px(450),
alignItems: 'center',
justifyContent: 'center',
marginTop: utils.px(50),
},ToastAndroid
原生的用于提示消息的方法,其实后面对应的是 anroid 的一个组件; 在 Android 设备上显示一个悬浮的提示信息 show 方法设置悬浮信息和时间 message 一个字符串,表示将要显示的文本内容。
duration 提示信息持续显示的时间。可以是 ToastAndroid.SHORT 或者 ToastAndroid.LONG
showWithGravity 的方法可以指定弹出的位置。可选项有:ToastAndroid.TOP, ToastAndroid.BOTTOM, ToastAndroid.CENTER.
showWithGravityAndOffset 综合的方法 showWithGravityAndOffset(message, duration, gravity, xOffset, yOffset)
javascript
import { View, StyleSheet, ToastAndroid, Button, StatusBar } from "react-native";
ToastAndroid.show("A pikachu appeared nearby !", ToastAndroid.SHORT);
};AppState
AppState 能告诉你应用当前是在前台还是在后台,并且能在状态变化的时候通知你
active - 应用正在前台运行
background - 应用正在后台运行。用户可能面对以下几种情况:
在别的应用中;
停留在桌面 ; 对 Android 来说还可能处在另一个 Activity 中(即便是由你的应用拉起的);
const appStateListner=()=>(nextAppState) => {
console.log('nextAppState', nextAppState);
if (nextAppState == 'active') {
}
}
useEffect(() => {
const subscription = AppState.addEventListener('change', appStateListner);
//退出页面的时候移除监听
return () => {
subscription.remove();
};
}, []);应用场景:多应用中的跳转,比如收藏列表中点击跳到直播,然后又返回;
定时器
用的较多的是这两个
setTimeout, clearTimeout
setInterval, clearInterval 需要注意的是在卸载组件前一定要清除定时器,要不然可能存在应用退出了,但是定时器还在运行的情况;
useEffect(() => {
//在初始化render之后只执行一次,在这个方法内,可以访问任何组件,、、
console.log("[App.js]---componentDidMount");
this.timer = setTimeout(() => {
setCount(1)
}, 2000);
return () => {
console.log("[App.js]---componentWillUnmount---");
// 如果存在this.timer,则使用clearTimeout清空。
// 如果你使用多个timer,那么用多个变量,或者用个数组来保存引用,然后逐个clear
this.timer && clearTimeout(this.timer);
};
}, []);按键监听
应用场景:比如按左键焦点要回到某个指定位置
javascript
import { TVEventHandler } from "react-native";
let tvEventHandler = null;
useEffect(() => {
//在初始化render之后只执行一次,在这个方法内,可以访问任何组件,、、
console.log("[App.js]---componentDidMount");
this.timer = setTimeout(() => {
setCount(1);
}, 2000);
setTvHandler();
return () => {
console.log("[App.js]---componentWillUnmount---");
// 如果存在this.timer,则使用clearTimeout清空。
// 如果你使用多个timer,那么用多个变量,或者用个数组来保存引用,然后逐个clear
this.timer && clearTimeout(this.timer);
disableTvHandler();
};
}, []);
//去掉按键捕获
disableTvHandler = () => {
if (tvEventHandler) {
console.log(" tvEventHandler.disable");
tvEventHandler.disable();
tvEventHandler = null;
}
};
setTvHandler = () => {
console.log("vip setTvHandler");
if (tvEventHandler) return;
this.tvEventHandler = new TVEventHandler();
this.tvEventHandler.enable(this, (component, event) => {
const { eventKeyAction, eventType } = event;
console.log("vip setTvHandler eventType=", eventKeyAction, eventType);
if (eventKeyAction === 0) {
switch (eventType) {
case "left":
...
break;
case "right":
...
break;
}
}
});
};全局变量
相当于 web 里的 world 类似,可以作为应用的全局缓存,每个页面都可直接使用,应用退出就没有了;
比如全局存储当前登录的用户信息;
global[APPNAME]['user'] = {};
作业
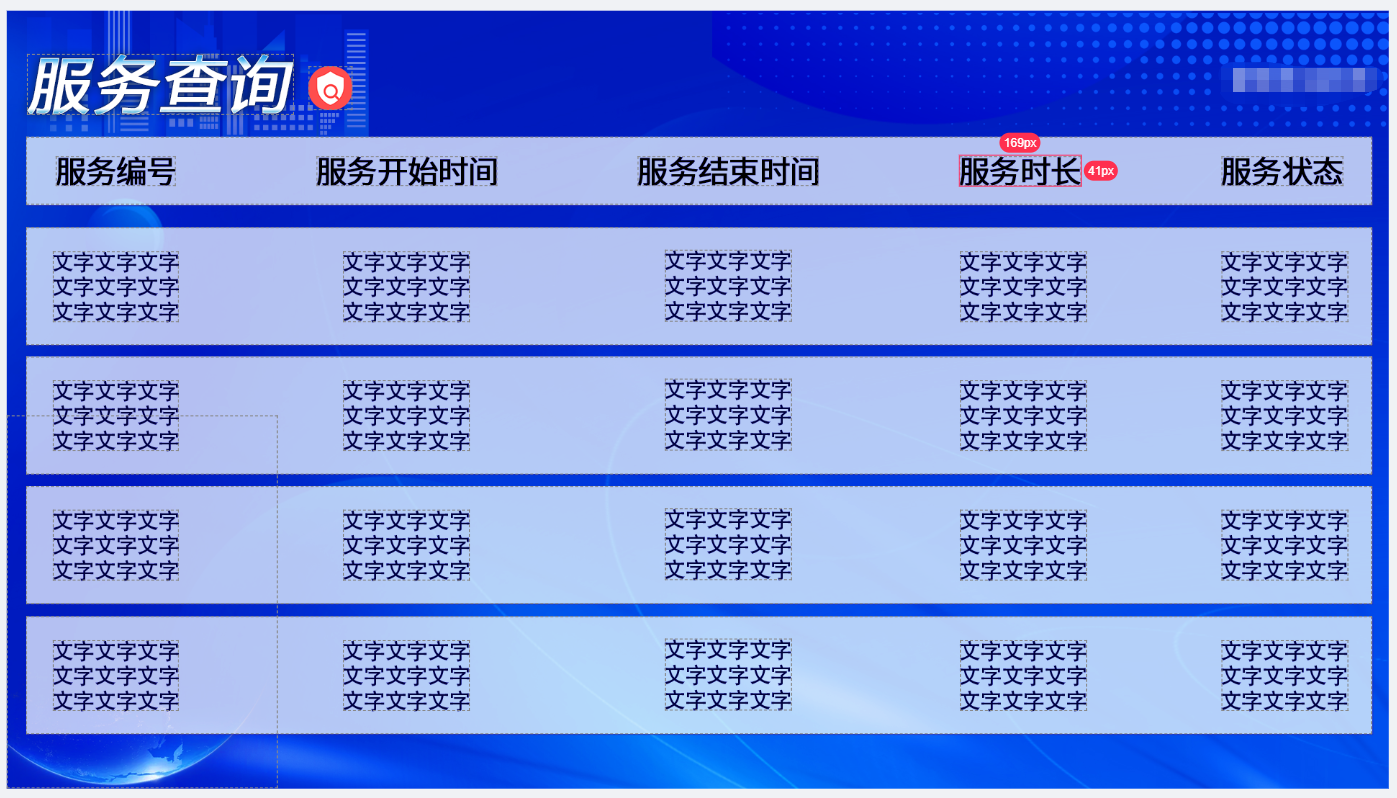 如图:
如图:
基本信息:页面尺寸 1920*1080
表格标题,#000000 字号 43,表格行高度 95,宽度 1870
文字内容,#030919 字号 31,文字行高度 164,宽度 1870,背景色:#FCFCFC,行之间间隔 16
1,数据任意, 2,每页显示 4 条记录,总共 10 条记录,可滚动;